
NASA’s Kepler space telescope has witnessed the effects of a dead star bending the light of its companion star. The findings are among the first detections of this phenomenon—a result of Einstein’s general theory of relativity—in binary, or double, star systems.
The dead star, called a white dwarf, is the burnt-out core of what used to be a star like our Sun. It is locked in an orbiting dance with its partner, a small “red dwarf” star. While the tiny white dwarf is physically smaller than the red dwarf, it is more massive.
“This white dwarf is about the size of Earth but has the mass of the Sun,” said Phil Muirhead of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, lead author of the findings to be published April 20 in the Astrophysical Journal. “It’s so hefty that the red dwarf, though larger in physical size, is circling around the white dwarf.”
Kepler’s primary job is to scan stars in search of orbiting planets. As the planets pass by, they block the starlight by miniscule amounts, which Kepler’s sensitive detectors can see.
“The technique is equivalent to spotting a flea on a light bulb 3,000 miles away, roughly the distance from Los Angeles to New York City,” said Avi Shporer, co-author of the study, also of Caltech.
Muirhead and his colleagues regularly use public Kepler data to search for and confirm planets around smaller stars, the red dwarfs, also known as M dwarfs. These stars are cooler and redder than our yellow Sun. When the team first looked at the Kepler data for a target called KOI-256, they thought they were looking at a huge gas giant planet eclipsing the red dwarf.
“We saw what appeared to be huge dips in the light from the star, and suspected it was from a giant planet, roughly the size of Jupiter, passing in front,” said Muirhead.
To learn more about the star system, Muirhead and his colleagues turned to the Hale Telescope at Palomar Observatory near San Diego. Using a technique called radial velocity, they discovered that the red dwarf was wobbling around like a spinning top. The wobble was far too big to be caused by the tug of a planet. That is when they knew they were looking at a massive white dwarf passing behind the red dwarf, rather than a gas giant passing in front.
The team also incorporated ultraviolet measurements of KOI-256 taken by the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), a NASA space telescope now operated by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. The GALEX observations, led by Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., are part of an ongoing program to measure ultraviolet activity in all the stars in Kepler’s field of view, an indicator of potential habitability for planets in the systems. These data revealed the red dwarf is very active, consistent with being “spun-up” by the orbit of the more massive white dwarf.
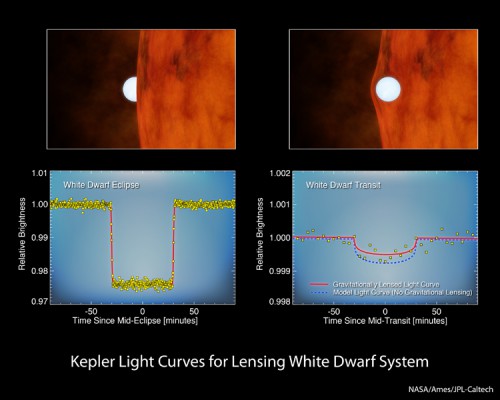
The astronomers then went back to the Kepler data and were surprised by what they saw. When the white dwarf passed in front of its star, its gravity caused the starlight to bend and brighten by measurable effects.
“Only Kepler could detect this tiny, tiny effect,” said Doug Hudgins, the Kepler program scientist at NASA Headquarters, Washington. “But with this detection, we are witnessing Einstein’s general theory of relativity at play in a far-flung star system.”
One of the consequences of Einstein’s general theory of relativity is that gravity bends light. Astronomers regularly observe this phenomenon, often called gravitational lensing, in our galaxy and beyond. For example, the light from a distant galaxy can be bent and magnified by matter in front of it. This reveals new information about dark matter and dark energy, two mysterious ingredients in our universe.
Gravitational lensing has also been used to discover new planets and hunt for free-floating planets.
In the new Kepler study, scientists used the gravitational lensing to determine the mass of the white dwarf. By combining this information with all the data they acquired, the scientists were also able to measure accurately the mass of the red dwarf and the physical sizes of both stars. Kepler’s data and Einstein’s theory of relativity have together led to a better understanding of how binary stars evolve.
Other authors include Andrew Vanderburg of the University of California, Berkeley; Avi Shporer, Juliette Becker, Jonathan J. Swift, Sasha Hinkley, J. Sebastian Pineda, Michael Bottom, Christoph Baranec, Reed Riddle, Shriharsh P. Tendulkar, Khanh Bui, Richard Dekany, and John Asher Johnson of Caltech; James P. Lloyd and Jim Fuller of Cornell University; Ming Zhao of The Pennsylvania State University, University Park; Andrew W. Howard of University of Hawaii, Hilo; Kaspar von Braun of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Germany; Tabetha S. Boyajian of Yale University, New Haven, Conn.; Nicholas Law of the University of Toronto, Canada; A. N. Ramaprakash, Mahesh Burse, Pravin Chordia, Hillol Das, and Sujit Punnadi of the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy & Astrophysics, India.
NASA Ames manages Kepler’s ground system development, mission operations, and science data analysis. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., managed Kepler mission development. Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colo., developed the Kepler flight system and supports mission operations with JPL at the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado in Boulder. The Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore archives, hosts, and distributes the Kepler science data. Kepler is NASA’s 10th Discovery Mission and is funded by NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s headquarters. JPL is a division of Caltech. For more information about the Kepler mission, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/kepler
This article was written by Whitney Clavin with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Gravity-Bending
Want to keep up-to-date with all things space? Be sure to “Like” AmericaSpace on Facebook and follow us on Twitter:@AmericaSpace



